Eliminate Risk of Failure with CIPS L4M2 Exam Dumps
Schedule your time wisely to provide yourself sufficient time each day to prepare for the CIPS L4M2 exam. Make time each day to study in a quiet place, as you'll need to thoroughly cover the material for the Defining Business Needs exam. Our actual Level 4 Diploma in Procurement and Supply exam dumps help you in your preparation. Prepare for the CIPS L4M2 exam with our L4M2 dumps every day if you want to succeed on your first try.
All Study Materials
Instant Downloads
24/7 costomer support
Satisfaction Guaranteed
A procurement organisation is keen to encourage innovation available within the supply market in the execution of an upcoming significant contract opportunity. A team member suggests that the specification should define the performance indicators so that supplier's solution can be checked against them. Which of the following will enable the organisation to achieve this goal?
See the explanation below.
The buying organisation is keen to encourage innovation so they should use the outcome or output based specification. In an outcome-based specification, umbrella statements like 'good quality', 'ambient temperature', 'convenient way' are often used. This may confuse the suppliers, and it's hard to check the solution that supplier offers. On the other hand, ouput-based specifications often include measurable requirements. For example, a specification for air conditioning system states that the system should maintain the room temperature at 19-24 degrees Celsius. Therefore, output specification is more appropriate in this case.
LO 3, AC 3.1
A company has a lists of items that make up 15% of total spend. These items also do not largely impact on quality of final product. The supply continuity is secured. Which of the following will be the most appropriate managing approach to purchase these items?
See the explanation below.
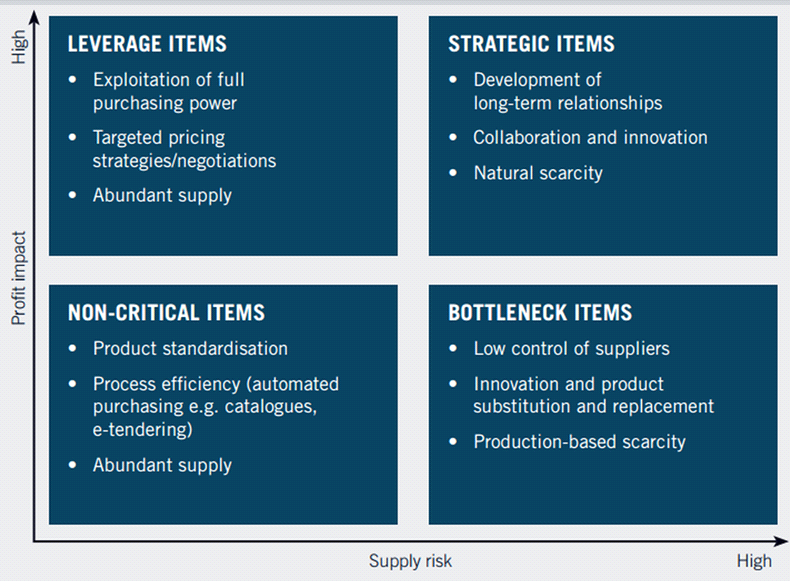
Those items make up small portion of spend and the supply risk is low. So it is tactical item according to Kraljic portfolio matrix. Procurement should bundle these items into larger contracts, simplify procurement process.
LO 2, AC 2.1
In 2016, ANA Airlines had to cancel some of its flight. The airline said it had discovered the cracks to the jet engine turbine blades. What should ANA procurement team do next to solve this problem?
See the explanation below.
Cracks on the jet engine is a closed-end problem. A typical problem solving process has 8 steps:
Step 1: Define the Problem
- What is the problem?
- How did you discover the problem?
- When did the problem start and how long has this problem been going on?
- Is there enough data available to contain the problem and prevent it from getting passed to the next process step? If yes, contain the problem.
Step 2: Clarify the Problem
- What data is available or needed to help clarify, or fully understand the problem?
- Is it a top priority to resolve the problem at this point in time?
- Are additional resources required to clarify the problem? If yes, elevate the problem to your leader to help locate the right resources and form a team.
- Consider a Lean Event (Do-it, Burst, RPI, Project).
- Ensure the problem is contained and does not get passed to the next process step.
Step 3: Define the Goals
- What is your end goal or desired future state?
- What will you accomplish if you fix this problem?
- What is the desired timeline for solving this problem?
Step 4: Identify Root Cause of the Problem
- Identify possible causes of the problem.
- Prioritize possible root causes of the problem.
- What information or data is there to validate the root cause?
Step 5: Develop Action Plan
- Generate a list of actions required to address the root cause and prevent problem from getting to others.
- Assign an owner and timeline to each action.
- Status actions to ensure completion.
Step 6: Execute Action Plan
- Implement action plan to address the root cause.
- Verify actions are completed.
Step 7: Evaluate the Results
- Monitor and Collect Data.
- Did you meet your goals defined in step 3? If not, repeate th 8-Step Process.
- Were there any unforeseen consequences?
- If problem is resolved, remove activities that were added previously to contain the problem.
Step 8: Continuously Improve
- Look for additional opportunities to implement solution.
- Ensure problem will not come back and communicate lessons learned.
- If needed, repeat the 8-Step Problem Solving Process to drive further improvements.
ANA has already known what is going on, the next step they should adopt is collecting more infor-mation on the problem. If the airline is hurry to the solution, it may choose 'Generate options ad-dressing the issue'. The crack on turbine blade can be welded, or the airline replaces a new blade. However, jumping to solution without knowing the root cause does not completely solve the prob-lem. The root cause is unaddressed, then it may occur in the future. Therefore, the airline should still collect information to find the root cause, then remove it.
LO 1, AC 1.1
ABC Ltd has enormous investment in facilities and machinery. It also employs skilled workforce. To be profitable, the company has to produce at massive quantity. Which sector does ABC Ltd belong to?
See the explanation below.
In the scenario, ABC Ltd has the following characteristics:
- Large investment in facilities and machinery
- Access to skilled workforce
- Mass production.
This company is a manufacturer. Manufacturing is an industry that makes products from raw ma-terials by the use of manual labour or machinery and that is usually carried out systematically with a division of labour.
Manufacturing requires investment in machinery and access to a suitably skilled workforce as well as materials and components.
- CIPS study guide page 74-76
- manufacturing | Definition, Types, & Facts | Britannica
LO 2, AC 2.1
A company buys components from its supplier. However, the supplier has not sent the invoice to the buyer and the buyer will not pay until next month. How will that amount of money be shown in the financial statements of the buying organization?
See the explanation below.
The buyer won't pay the supplier until next month. This is a liability to the buyer. This amount can be recorded as accrued expense or accounts payable. On the other hand, the supplier has not sent the invoice, so it should be accrued expense.
Both accounts payables and accrued expenses are liabilities. Accounts payable is the total amount of short-term obligations or debt a company has to pay to its creditors for goods or services bought on credit. With accounts payables, the vendor's or supplier's invoices have been received and recorded.
On the other hand, accrued expenses are the total liability that is payable for goods and services that have been consumed by the company or received. However, accrued expenses are those bills in which an invoice or bill has not yet been received. As a result, accrued expenses can sometimes be an estimated amount of what's owed, which is adjusted later to the exact amount, once the invoice has been received.
Conversely, accounts payable should represent the exact amount of the total owed from all of the invoices received.
- CIPS study guide page 55-56
- Understanding Accrued Expenses vs. Accounts Payable (investopedia.com)
LO 1, AC 1.4
Are You Looking for More Updated and Actual CIPS L4M2 Exam Questions?
If you want a more premium set of actual CIPS L4M2 Exam Questions then you can get them at the most affordable price. Premium Level 4 Diploma in Procurement and Supply exam questions are based on the official syllabus of the CIPS L4M2 exam. They also have a high probability of coming up in the actual Defining Business Needs exam.
You will also get free updates for 90 days with our premium CIPS L4M2 exam. If there is a change in the syllabus of CIPS L4M2 exam our subject matter experts always update it accordingly.
