Eliminate Risk of Failure with AICPA-Business Exam Dumps
Schedule your time wisely to provide yourself sufficient time each day to prepare for the AICPA-Business exam. Make time each day to study in a quiet place, as you'll need to thoroughly cover the material for the CPA Business Environment and Concepts exam. Our actual Certified Public Accountant exam dumps help you in your preparation. Prepare for the AICPA-Business exam with our CPA-Business dumps every day if you want to succeed on your first try.
All Study Materials
Instant Downloads
24/7 costomer support
Satisfaction Guaranteed
Williams, Inc. is interested in measuring its overall cost of capital and has gathered the following data. Under the terms described below, the company can sell unlimited amounts of all instruments.
* Williams can raise cash by selling $1,000, 8 percent, 20-year bonds with annual interest payments.
In selling the issue, an average premium of $30 per bond would be received, and the firm must pay floatation costs of $30 per bond. The after-tax cost of funds is estimated to be 4.8 percent.
* Williams can sell 8 percent preferred stock at par value, $105 per share. The cost of issuing and selling the preferred stock is expected to be $5 per share.
* Williams' common stock is currently selling for $100 per share. The firm expects to pay cash dividends of $7 per share next year, and the dividends are expected to remain constant. The stock will have to be underpriced by $3 per share, and floatation costs are expected to amount to $5 per share.
* Williams expects to have available $100,000 of retained earnings in the coming year; once these retained earnings are exhausted, the firm will use new common stock as the form of common stock equity financing.
* Williams' preferred capital structure is:
Long-term debt 30%
Preferred stock 20
Common stock 50
The cost of funds from retained earnings for Williams, Inc. is:
See the explanation below.
Choice 'a' is correct. 7.0 percent cost of funds from retained earnings.
The cost of retained earnings is equal to the rate of return required by the firm's common shareholders (or, in effect, the return 'lost' by them when the firm chooses to fund with retained earnings). While oftentimes this rate is somewhat subjective, we are given the facts to exactly answer the question in this case. The stock is currently selling for $100/share, and the dividend is given at $7/share.
$7 / $100 = 7%
Choices 'b', 'c', and 'd' are incorrect, per the above Explanation:/calculation.
The following information pertains to Quest Co.'s Gold Division for 1993:

Quest's return on investment was:
See the explanation below.
Choice 'c' is correct. Return on investment equals net income divided by average invested capital:
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect, per the above calculation.
Select Co. had the following 1994 financial statement relationships:
Asset turnover 5
Profit margin on sales 0.02
What was Select's 1994 percentage return on assets?
See the explanation below.
Choice 'd' is correct. Return on assets equals income divided by average assets. This formula can be further divided into the components of profit margin times asset turnover (referred to as the Dupont formula):
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'c' are incorrect, per the above calculation.
The following selected data pertain to the Darwin Division of Beagle Co. for 1994:
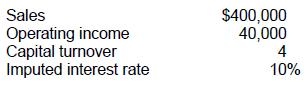
What was Darwin's 1994 residual income?
See the explanation below.
Choice 'd' is correct. Residual income is income less the imputed interest rate times average invested capital. Capital turnover is equal to sales / average invested capital.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Residual income is greater than zero. The imputed interest rate times average invested capital needs to be compared with operating income.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Residual income is not simply the imputed interest rate times operating income.
The imputed interest rate times average invested capital needs to be compared with operating income.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. Residual income is not simply imputed interest rate times average invested capital. The operating income must be considered.
One approach to measuring divisional performance is return on investment. Return on investment is expressed as operating income:
See the explanation below.
Choice 'd' is correct. Return on investment is operating income divided by total assets.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Current year's capital expenditures plus cost of capital would be a meaningless denominator.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. This omits the current assets employed by the division.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. This omits fixed assets.
Are You Looking for More Updated and Actual AICPA-Business Exam Questions?
If you want a more premium set of actual AICPA-Business Exam Questions then you can get them at the most affordable price. Premium Certified Public Accountant exam questions are based on the official syllabus of the AICPA-Business exam. They also have a high probability of coming up in the actual CPA Business Environment and Concepts exam.
You will also get free updates for 90 days with our premium AICPA-Business exam. If there is a change in the syllabus of AICPA-Business exam our subject matter experts always update it accordingly.
